An Open Letter to the Triangle Swing Dance Scene re: the Continuation of RDU Rent Party
Dear friends and fellow dancers,
I am writing to you today to seek your input and guidance on the future of RDU Rent Party dance events. Laura Windley and I have been running these live music dances now for several years now to sometimes great success. Lately, however, we have seen smaller numbers of dancers showing up at Rent Party events and smaller amounts showing up in the hat box. This lull is starting to make it very hard to pay musicians a reasonable wage and as such we are currently considering whether or not to put Rent Party on hiatus. We have always thought of RDU Rent Party as a community event and so we felt it best to offer an open discussion with the Triangle Swing Dance community before making any decisive moves on this subject.
A little back story
For those not familiar with it, RDU Rent Party exists as a labor of love for myself and Laura, we host bands for a pay-what-you-can dance, I pay for the space rental out of my own pocket, and all money collected is given to the band. We frequently pick up travelling bands on tour because we can offer them an extra gig on an off night (typically Thursdays). Laura and I started this at a time when the local swing dance society (TSDS) was in a financial crisis and typically hiring cheap bands over what we would consider to be good bands. In the past year or two TSDS has started hiring what we think are more exciting bands and is back on solid financial ground and we have seen a slow decline in RP numbers in the meantime. Whether or not these are related is questionable but it does leave us questioning if RDU Rent Party still has a role to play in the swing scene as it stands.
If you want a bit more backstory, you can check out this post I wrote a while back on the history of RP.
RP’s place as we see it
So approximately speaking, this is where we have seen the place of Rent Party dances in our local scene in past:
- Rent Party has been able to bring in bands that often would not be here on a weekend, meaning we wouldn’t get to hear them play or dance to them unless they happened to get a bar gig of some sort. Because TSDS only hosts Saturday night dances, we would miss many of these bands on tour because they are usually already booked for weekend gigs at exchanges and workshops.
- Rent Party has at times been able to work with bands who are otherwise prohibitively expensive because we can work with them on an off night.
- Rent Party has been able to serve as a testing ground for several bands which the local swing dance society would be hesitant to try untested. Several bands like Bumper Jacksons, Clark Stern, and Hot Club of North Carolina have since gone on to play to larger crowds at our local Saturday night dances. We also put on the first ever dance played by the now infamous Mint Julep Jazz Band.
- Rent Party has kept a place for live music in the center of the Triangle area where dancers can still easily mix and pull from Raleigh, Durham, and Chapel Hill. At this point, TSDS has only been able to find suitable venues in the far West end of the Triangle.
- And finally, Rent Party remains able to host dances that simply would not fly at TSDS dances. Having solo piano badass, Ethan Uslan, play alone for a packed house of dancers or Soul DJ, Ryan Thomas, spin a whole night of vintage vinyl, for instance would not happen anywhere else in the Triangle.
The situation as it stands
In the last year or so we have seen RP numbers drop in a not-insignificant fashion. I would estimate we are seeing 2/3 of the numbers at the door and close to half of the money in the hat box meaning not only are fewer people showing up, but they are also paying in less. While I’m happy to lose money on the event and put on an awesome show, the host in me can’t really continue to be excited at the prospect of underpaying the musicians we offer gigs to. RP has slowly become a more stressful experience when we once easily paid 7 or 8 people a solid wage and now struggle to pay 4 decently. Not only that, but it hinders our ability to bring in bands when the range we can reasonably promise them continues to shrink. At the moment we have several bands from Philly and NYC who have asked to play but for whom the current RP numbers aren’t worthwhile.
We need your input
We put on RP for our own enjoyment and hopefully for the good of the community. Laura and I are happy to continue to invest in Rent Party, and we think bands are happy to invest their time in it as well, so long as the community can match that energy. We are also happy to let it rest and focus our energies elsewhere if RDU Rent Party has run its course. But we don’t want to make this decision alone, so please let us know what you think, either in the comments or by emailing me. If you want to see RDU Rent Party continue or if you have ideas on how we could make it more enticing for you both to show up and to show the bands some love, we are happy to hear them. Or if you feel like in a sea of good options lately, that RP just doesn’t draw you like it used to and we should take a break, we’d love to hear that too.
Regardless, we are grateful for the approximately 3-4 year run that we have had, to all the dancers who made it possible, to all the bands who tried this crazy idea with us, and for all the amazing experiences it has allowed us to have. Whatever decision we end up making, know that we are extremely grateful for the good times and happy to make our future endeavors whatever will serve the dance and the scene best.
Cheers,
Jason & Laura





 It’s an idea many of us have heard or even expressed ourselves in learning to dance: it’s important to tape yourself. While it’s an easy concept to understand, I have never seen it illustrated so clearly as I have recently with a couple of new students. Working with them has been a great education for me in seeing how powerful the idea of taping yourself can be.
It’s an idea many of us have heard or even expressed ourselves in learning to dance: it’s important to tape yourself. While it’s an easy concept to understand, I have never seen it illustrated so clearly as I have recently with a couple of new students. Working with them has been a great education for me in seeing how powerful the idea of taping yourself can be.


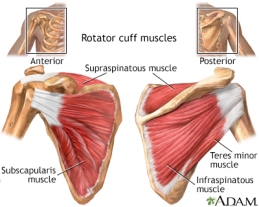
 I see the same effect on my Rolfing® table where many people’s bodies tense away from the table almost as if they could levitate themselves by sheer force of will. When I prompt them to recognize that the table can support their weight and to let themselves sink into that support, their bodies relax and their mental state follows suit shortly after. In standing, a similar effect is achievable by becoming aware of the bones in your body and allowing weight to carry through bones rather than be held up by muscle.
I see the same effect on my Rolfing® table where many people’s bodies tense away from the table almost as if they could levitate themselves by sheer force of will. When I prompt them to recognize that the table can support their weight and to let themselves sink into that support, their bodies relax and their mental state follows suit shortly after. In standing, a similar effect is achievable by becoming aware of the bones in your body and allowing weight to carry through bones rather than be held up by muscle.

